Study Guide
Field 162: Earth Science
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Sample Selected-Response Questions
The following reference materials will be available to you during the test:
Competency 0001
Space Systems
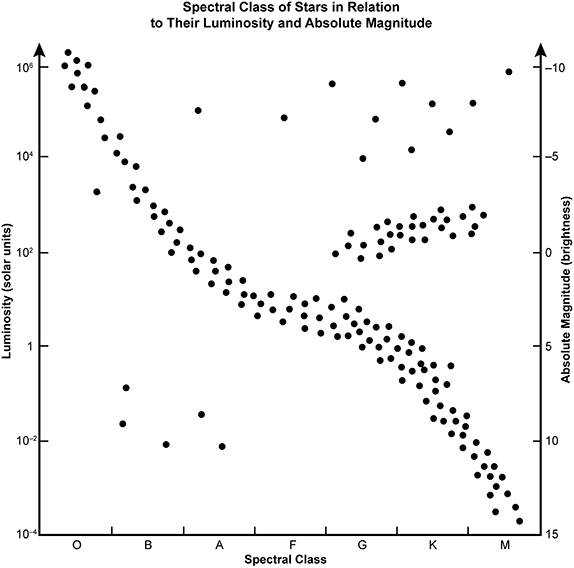
1. Use the H-R diagram below to answer the question that follows.
A Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is shown with the title spectral class of stars in relation to their luminosity and absolute magnitude. The x-axis is labeled Spectral Class and there are two y-axes, one labeled luminosity in solar units and the other labeled absolute magnitude of brightness. There are four groups of stars, the largest of which runs from spectral class O at 1,000,000 solar units at the top left of the graph diagonally toward the bottom right of the diagram. It levels off mid-way across the graph around spectral class A, F, and G at 100 to 1 solar units before finishing curving to the bottom right of the graph at spectral class M and 10 to the negative fourth power solar units. The next group is a loose cluster along the top of the graph from spectral class A, through F, G, K, and M and between 1,000,000 and 10,000 solar units. The third group is a tight cluster through spectral class G, K, and M and between 1,000 and 100 solar units. The final group is a loose cluster near the bottom left of the graph in spectral class B and A that is between one tenth and one one-hundredth solar units.
Which spectral class would most likely be used to classify a medium-sized yellow star, such as the Sun, at the very end of its life cycle?
- A
- F
- M
- K
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate knowledge of the life cycles of different types of stars and use models such as the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. As its life cycle progresses, a medium-sized yellow star like the sun expands into a red giant. Then, once the star has consumed all usable nuclear fuel, it collapses into a stellar body known as a white dwarf. This stage in the evolution of a star is associated with spectral class A in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Stars found in this spectral group are fainter than main sequence stars.
Competency 0001
Space Systems
2. The observable differences in the composition of the inner and outer planets are a result of the solar system's formation process. Which statement most accurately describes the primary cause of these differences?
- The Sun drew heavier compounds inward due to its gravitational field.
- The substances close to the Sun accumulated easily because of their high density.
- The lighter elements moved outward from the Sun due to centrifugal forces.
- The Sun vaporized nearby substances because of their low condensation temperatures.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate knowledge of current theories of the origin of the solar system and composition of all types of matter in the universe. During the evolution of the solar system, the inner planets were exposed to high temperatures associated with the protosun and only substances with a high condensation point, such as metals and various minerals, were able to condense and thus serve as "seeds" around which accretion occurred. The outer planets were located far from the protosun in a region where lower temperatures allowed hydrogen compounds to condense and capture the gases in the process that resulted in the formation of the outer planets. There were relatively small amounts of rock and metals that condensed in the outer planets as well.
Competency 0001
Space Systems
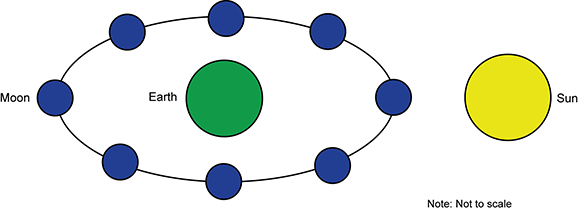
3. Directions: Examine the diagram below of the Earth-Sun-Moon system. Click on the position of the moon where a person on Earth in the Northern Hemisphere would observe a waxing crescent moon.
A diagram of the Earth-Sun-Moon system is shown with the Moon orbiting the Earth. The moon is shown in eight distinct positions. One position is directly between the Earth and the Sun, then the other positions are evenly spaced along the lunar orbit.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
-
Correct Response: Top right position.
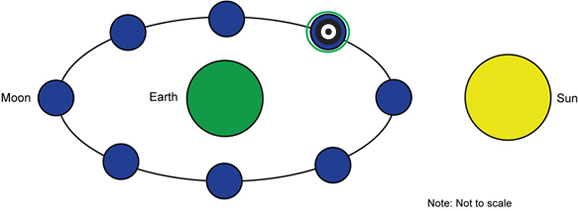
A diagram of the Earth-Sun-Moon system is shown with the Moon orbiting the Earth. The moon is shown in eight distinct positions. One position is directly between the Earth and the Sun, then the other positions are evenly spaced along the lunar orbit. The top right position is marked with a target, indicating it as the chosen response.
This item requires the candidate to analyze how the relative motions and interactions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon result in the observed patterns of phases of the Moon, eclipses, and tides. When the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun, the light from the Sun hits the Moon on the opposite side of the Moon than the Earth can observe. This results in a new Moon. The Moon then revolves around the Earth, to the top-right position, so that part of the Moon's light side is observed in a thin curve on the right side as viewed from Earth. This is a waxing crescent moon.
Competency 0002
Earth Materials and the History of Earth
4. Many minerals have characteristic crystal forms, but these forms are not always observable in crystals found in nature because:
- weathering after formation breaks down the crystal form of minerals.
- most minerals have impurities that alter their crystal forms.
- cooling of lava and crystal formation of minerals occur at uneven rates.
- strong molecular bonds change the crystal form of minerals.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics used to classify minerals. The characteristic crystal forms associated with specific minerals depends on the underlying type and arrangement of atoms. In nature the presence of a different type of atom usually interrupts the repeating pattern that underlies the crystalline structure, which alters the observable crystal structure.
Competency 0002
Earth Materials and the History of Earth
5. A sharp break in seismic velocity occurs at the Mohorovicic discontinuity. Which statement best describes the cause of this discontinuity?
- The discontinuity defines the boundary with a layer of lower-density rock above and a layer of higher-density rock below.
- The discontinuity defines the boundary that represents a change in viscosity from more rigid rock above to more viscous rock below.
- The discontinuity defines the boundary with a layer of rock with a smaller volume above and a layer of rock with a larger volume below.
- The discontinuity defines the boundary that represents the area where high pressures convert liquid rock above to solid rock below.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. This item requires the candidate to demonstrate knowledge of Earth's layered structure and composition and the use of seismological tools and data to investigate Earth's interior. The discovery of the Mohorovicic discontinuity was based on the observations that seismic waves traveled slower when moving through the Earth's upper mantle compared to its crust. This difference in speed is evidence of the presence of an underlying layer of the Earth with different physical properties than that of the crust, specifically a layer of Earth with a higher density.
Competency 0003
Geologic Systems
6. In comparison to shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by intermittent and explosive eruptions that eject lava and ash high into the air. This type of eruptive activity gives stratovolcanoes their conical shape. Which factor is a vital contribution to these characteristics?
- high amounts of mafic material
- low viscosity of flowing magma
- high water content
- low silica content
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. This item requires the candidate to analyze the results of the interactions of plate boundaries, including volcanic eruptions. Stratovolcanoes are usually associated with subduction zones where oceanic crust is drawn under continental crust. In this type of volcano, as magma is formed it contains water in the form of hydrated minerals and in the basalt rock of the ocean crust. In addition to other dissolved gases, once a critical level of water accumulates within the volcano, a sudden explosive eruption takes place.
Competency 0003
Geologic Systems
7. Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
Line Mountain Glaciers Mountain Streams 1 They carry eroded material down the mountain. Eroded material is deposited at stream edges where velocity is lowest. 2 Erosion of soil and loose rock is more efficient due to presence of solid ice and snow. Erosion of soil and loose rock is less efficient because liquid water creates less friction. 3 They are seasonal, leaving the valley walls unprotected from other erosive processes. They are permanent and deposit eroded material that increases the thickness of the valley walls. 4 They erode both walls and floor of the valley, removing all loose material. They erode primarily the valley floor, leaving steep walls that are structurally unstable.
Mountain glaciers and mountain streams both tend to follow preexisting valleys during their descent down the slopes of a mountain. Which line in the table best explains why mountain glaciers tend to erode U-shaped valleys, while erosion from mountain streams produces V-shaped valleys?
- Line 1
- Line 2
- Line 3
- Line 4
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. This item requires the candidate to analyze the connection between erosion and deposition, different agents that cause erosion and deposition, and the ways in which these processes alter river systems and glaciated regions. V-shaped valleys are those that have steep valley walls and narrow valley floors. These types of valleys are formed as the result of fast-flowing water as it moves down steep mountain gradients, removing more sediment from the bottom of the river channel than from the sides of the valley. U-shaped valleys have steep walls with wide, curved valley floors that develop as rock and sediment that is carried by a slow-moving glacier scrapes against the existing valley floor.
Competency 0004
Water, Weather, and Climate
8. During a severe weeklong summer heat wave in the eastern United States, skies remain clear and overnight cooling is limited by high relative humidity. Under these atmospheric conditions, there is an absence of convection-fueled afternoon thunderstorms. Weather exhibited during this week is most likely the result of which condition?
- An upper-level inversion develops as a sinking air mass warms by compression and reduces atmospheric instability.
- The condensation of water vapor into dew at night dries out the near-surface air mass and increases its buoyancy.
- The circulation of winds in an upper-level high-pressure system increases shear and disrupts rising columns of the moist air mass.
- A near-surface air mass moving from bodies of water to land generates strong winds and reduces atmospheric mixing.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. This item requires the candidate to analyze variables that cause different types of weather, including the motion of air masses. Thunderstorms frequently form as the result of warm surface air interacting with cooler air higher in the atmosphere. In this example, vertical movement of warmed air near the ground is prevented from rising due to the formation of an upper level inversion.
Competency 0004
Water, Weather, and Climate
9. One projected consequence of global climate change is the possible disruption of the Gulf Stream, which conveys heat from the tropical Atlantic to the North Atlantic Ocean. Which statement most appropriately describes the mechanism that might slow or stop the movement of the Gulf Stream?
- Increased numbers of hurricanes and tropical storms pull energy that generates the flow of the Gulf Stream from the tropical ocean to the North Atlantic.
- Disproportionate warming of the equatorial Atlantic compared to the North Atlantic increases the thermal gradient between the two areas.
- Melting glaciers reduce salinity in the North Atlantic, preventing the sinking of salty water in that area that drives thermohaline circulation.
- Warming of the atmosphere in the North Atlantic reduces the intensity of the southern winds that push the waters of the Gulf Stream northward.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. This item requires the candidate to analyze global climate models of short- and long-term regional or global climate change and impacts to Earth systems. The movement of the Gulf Stream occurs because warmer water from the tropical Atlantic is less dense than cold water and thus forms an upper layer that continues moving to the North Atlantic Ocean. The density of the Gulf Stream increases as it begins to cool down, and in the North Atlantic Ocean this body of water sinks and begins to flow back to the south. Water contributed from melting glaciers, however, would dilute the salt content of the water and decrease its density. Thus, the Gulf Stream would be prevented from sinking and the thermohaline circulation process would not occur.
Competency 0005
Human Impacts and Sustainability
10. Across the globe, the demand for renewable energy in homes and businesses has increased significantly in recent years. However, the expansion of solar and wind power as reliable, stand-alone energy supply systems has been limited. Which challenge to the solar- and wind-power generation industries has been the primary factor that has limited the use of these energy systems?
- the shortage of manufacturing facilities producing solar panels and wind-generation systems
- the scarcity of large-scale electrochemical systems required to store electricity generated by solar and wind power for later use
- the lack of infrastructure required to connect multiple home solar and wind power systems together
- the inefficiency of transitioning direct current (DC) generated by solar and wind power to the alternating current (AC) needed for electricity use
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. This item requires the candidate to analyze the management and use of renewable natural resources. The electricity produced as the result of solar- and wind-powered systems fluctuates and may even vary seasonally in some geographical areas. Therefore, to have a reliable electricity supply, the electricity must be stored so that it may be used in times of low or no production. This requires a large financial commitment in order to adapt existing infrastructure or construct new electrochemical systems that can be used to store electricity for later use.
Competency 0005
Human Impacts and Sustainability
11. A town located near a volcano is experiencing frequent ash falls. An engineering team has been hired to implement steps to prevent the destruction of town buildings from ash accumulation. Which engineering design most effectively addresses the town's concerns and takes into account real-world constraints and solutions?
- demolishing and reconstructing all town buildings to strengthen structures, in order to support the weight of the ash
- manufacturing a large curved wall between the volcano and the town, in order to redirect the ash around the town buildings
- removing and replacing the roofs on town buildings to increase their pitch, in order to prevent ash buildup
- using automated robots to capture the ash, in order to stop it before it reaches any town building
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. This item requires the candidate to evaluate an engineering design solution, taking into account a range of constraints. Pitched roofs are stronger and more stable because volcanic ash slides down and off of the roof instead of accumulating, where the weight of the ash can cause damage to the roof and may even result in its collapse. This engineering design also is effective because the pattern of falling ash is not always predictable and is affected by factors such as prevailing winds, so building a wall would not help. Monetary and technological constraints make choices A and D unlikely.